As a core component of the CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing system, sgRNA guides the Cas9 protein to precisely cleave specific DNA sequences. The technical approaches for obtaining sgRNA continue to evolve, among which the scheme of high-throughput synthesis of Oligo Pools and in vitro preparation into sgRNA libraries, with its characteristics of scalability, low cost and flexible customization, has become the core choice for large-scale gene screening and genome-wide targeted research.
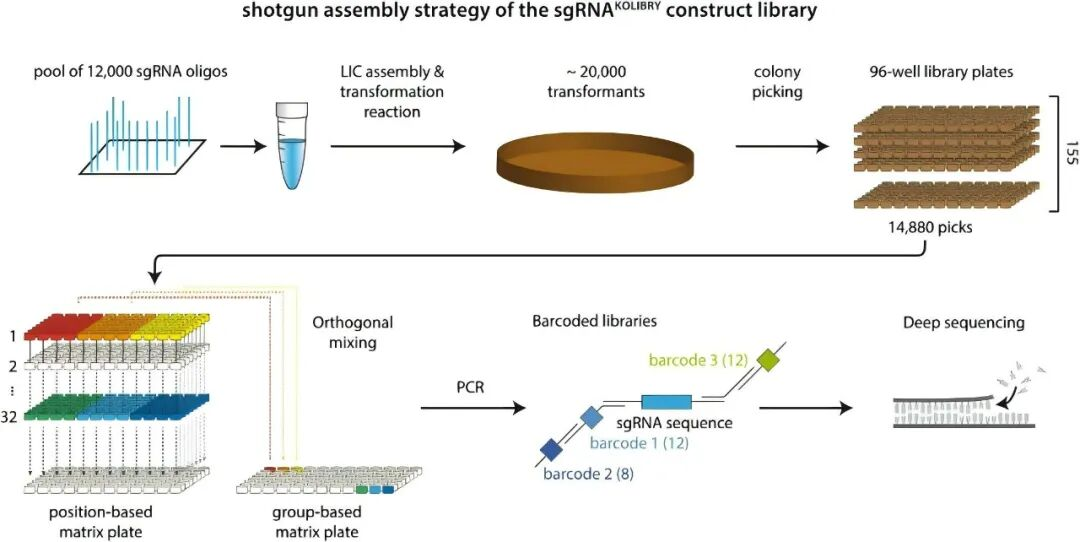
Figure 1. The construction process of sgRNA library based on chip-synthesized Oligo Pools [1]. With "efficient assembly-arrayed screening-orthogonal validation" as the core, researchers have achieved the construction of an arrayed sgRNA library covering nearly all human protein-coding genes through Ligation-Independent Cloning (LIC) technology and iterative optimization strategies.
After years of research and development, iGeneTech has launched the new-generation high-throughput DNA synthesis platform - Ignite 3.0. The high-quality Oligo Pools synthesized by this platform can lay a foundation for the efficient construction of sgRNA libraries and the reliability of experimental results.
Advantages of the Solution
01 Large-Scale Synthesis, Suitable for sgRNA Genome-Wide Library Construction
Ignite 3.0 can flexibly adapt to the synthesis of Oligo Pools of different sizes, ranging from 4k to 650k, with a synthesis length of up to 200 nt. It can synthesize thousands to hundreds of thousands of sgRNA-encoding Oligos targeting different genes in one go, directly meeting the requirements for sgRNA library construction. For example, for approximately 20,000 protein-coding genes in humans, 3-5 sgRNA sequences can be designed for each gene; through a single round of Oligo Pools synthesis, all genome-wide target sequences can be covered, greatly shortening the library construction cycle.
02 High Uniformity and Low Error Rate, Ensuring High-Quality sgRNA Library Construction
The single-Oligo yield of Oligo Pools synthesized by the Ignite 3.0 platform exceeds 0.5 fmol, and the 95%/5% percentile ratio is as low as 1.82. This ensures that each sequence is sampled equally in downstream screening, thereby improving the sensitivity of sgRNA screening.
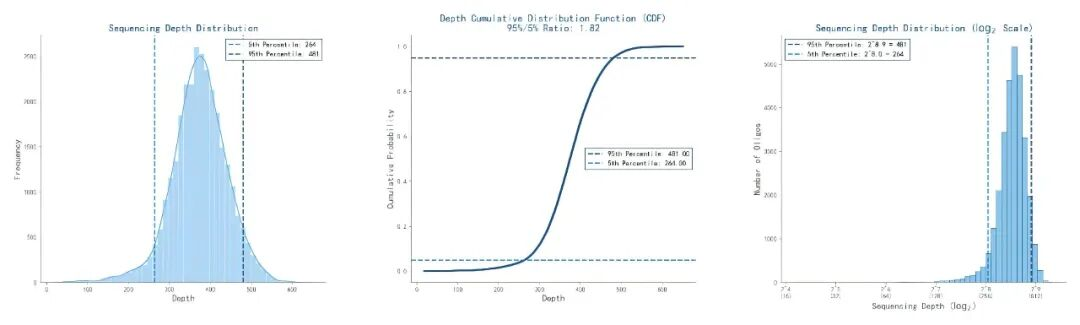
Figure 2. Uniformity Performance of Oligo Pools from the Ignite 3.0 Platform. The synthetic products of a 200nt oligonucleotide pool containing 30,000 unique sequences were amplified and subjected to Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS). The depth distribution of each oligonucleotide sequence in the pool was analyzed by counting the number of sequencing reads corresponding to each sequence.
The average single-base error rate (mismatches + insertions/deletions (indels)) of Oligo Pools synthesized by the Ignite 3.0 Platform is around 0.1%, which is far lower than the industry average. This low error rate can reduce errors in sgRNA sequences, thereby minimizing the probability of off-target effects at the source.
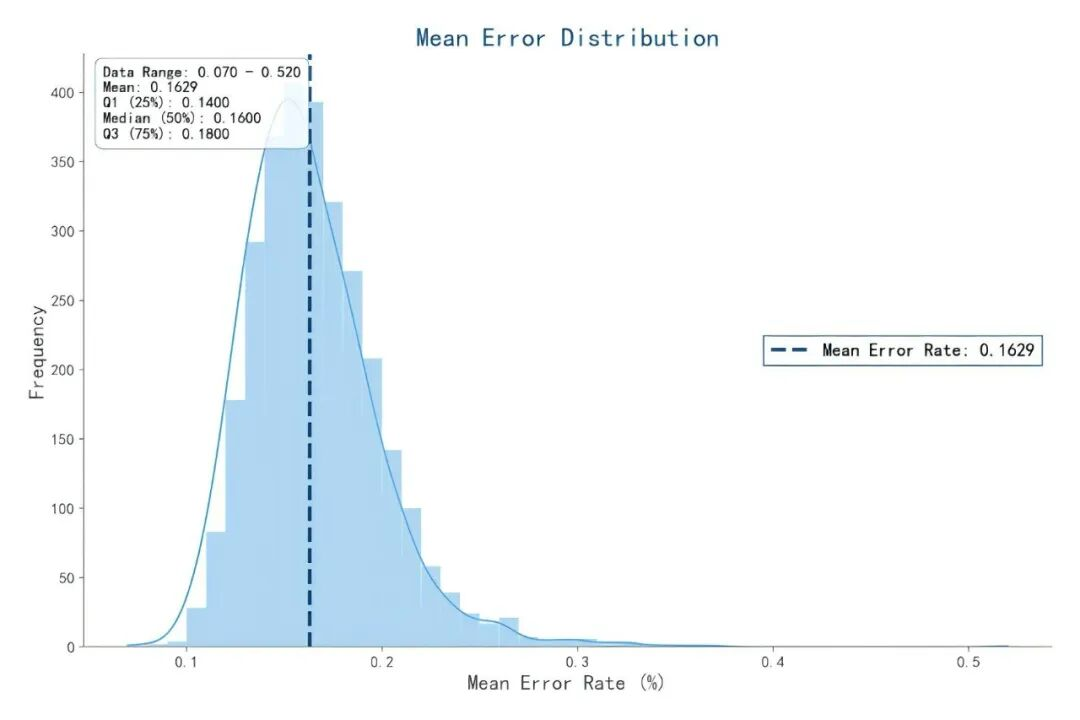
Figure 3. Synthesis Error Rate Performance of Oligo Pools from the Ignite 3.0 Platform. The synthetic products of 130 nt oligonucleotides with 3,000 unique sequences were amplified, and Unique Molecular Identifiers (UMIs) were added before amplification. After amplification, next-generation sequencing (NGS) was performed. Sequencing reads carrying the same UMI were clustered to generate Consensus Sequences, which were then compared with the original designed sequences. Detection results showed that the comprehensive error rate was only 0.1629% (including base substitutions, insertions, and deletions).
03 CRISPR Off-Target Detection Using TargetSeq/MultipSeq Capture Technologies
After years of technical research and development, iGeneTech has successfully established TargetSeq® hybrid capture sequencing technology and MultipSeq® multiplex amplicon sequencing technology, which can be applied to the detection of CRISPR/Cas9 off-target sites. This series of technologies enables simultaneous hybrid capture or amplification enrichment of the target editing site and hundreds of predicted off-target sites to generate a targeted capture library. Through sequencing and bioinformatics analysis, the mutation frequencies of the target site and off-target sites can be quantitatively analyzed.
Case Sharing
To evaluate the editing efficiency and off-target rate of sgRNA, researchers systematically assessed the impact of the 5' end length of sgRNA on the editing efficiency and specificity of CRISPR/Cas9. The results showed that the 5' end length of sgRNA could alter genome editing activity. In addition, the study verified off-target sites using a custom TargetSeq® Panel. This not only enabled sensitive detection of the activity and specificity of sgRNAs with different lengths, but also helped identify that off-target sites containing microsatellites would interfere with evaluation. Meanwhile, it was confirmed that sgRNA activity could be accurately detected at a sequencing depth of 300×, providing an effective technical method for the efficient evaluation of CRISPR sgRNA [2].

References
[1] Schmidt T , Schmid-Burgk J L , Hornung V .Synthesis of an arrayed sgRNA library targeting the human genome[J].Scientific Reports, 2015, 5:14987.DOI:10.1038/srep14987.
[2]Changzhi,Zhao,Yunlong,et al.Evaluation of the effects of sequence length and microsatellite instability on single-guide RNA activity and specificity.[J].International journal of biological sciences, 2019, 15(12):2641-2653.DOI:10.7150/ijbs.37152.

 CN
CN




