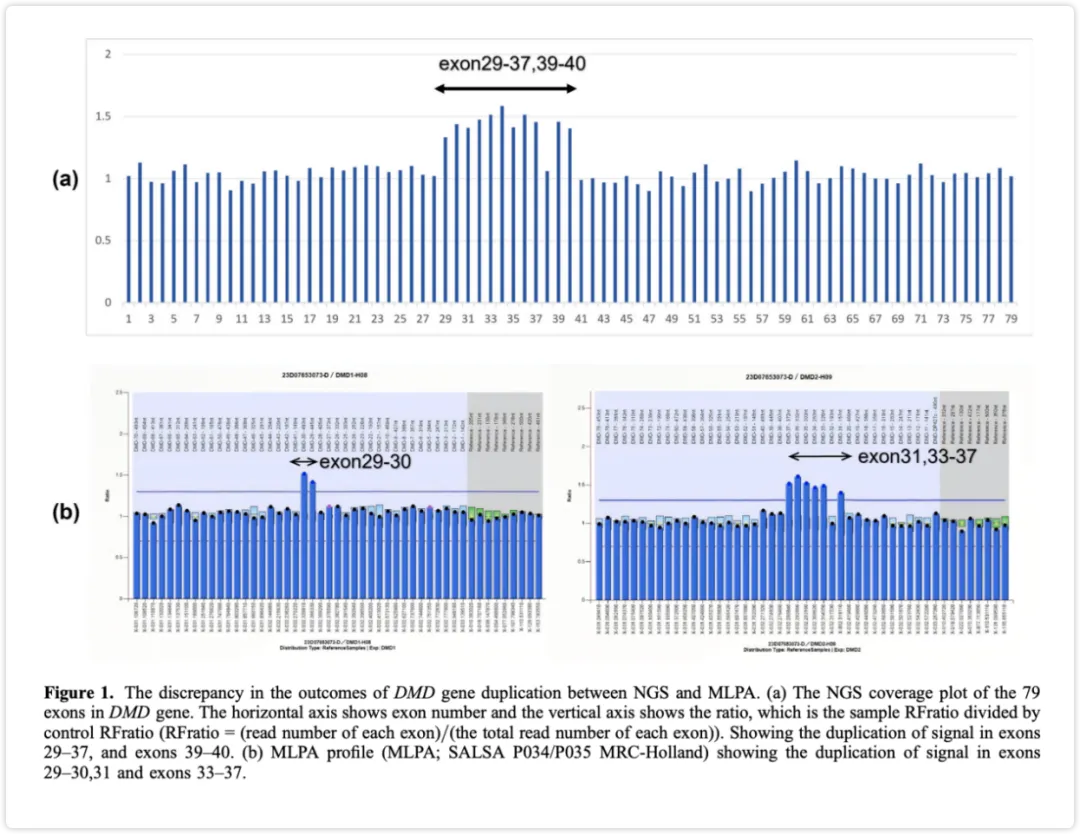
In July 2025, the Pathology Society of Chinese Medical Association and the National Center for Pathology Quality Control organized molecular pathology experts to formulate the Expert Consensus on Combined High-Throughput Sequencing Detection of Common Driver Genes (DNA and RNA) in Solid Tumors (2025 Edition). This consensus clarifies the clinical value and target population of combined DNA/RNA-NGS detection, the advantages and disadvantages of different combined detection strategies, and standardizes sample selection and quality control, library construction technology, bioinformatics analysis, and reporting standards. It aims to promote the standardized application of combined detection technology and provide a reliable basis for the precise diagnosis and treatment of solid tumors.
Clinical Application of DNA/RNA-NGS Detection in Tumor Mutation Detection:
DNA-NGS is efficient and accurate in detecting conventional mutation types such as SNVs, InDels, and CNVs. However, for fusion mutation detection, it requires separate design and coverage based on clear intronic information of fusion genes or known breakpoint information. Even so, since fusion events usually occur in complex intronic regions, it is difficult for Panel design to achieve the expected scheme of full coverage and high specificity for intronic regions.
RNA-NGS can enhance the flanking capture of probes at exon boundaries through a Panel design based on transcript reference sequences. It directly detects mRNA sequences after alternative splicing in RNA samples, avoiding intronic interference, thereby accurately identifying clinically relevant fusion transcripts and significantly improving the sensitivity of gene fusion detection.
Therefore, from the perspective of clinical research, for patients with negative fusion detection by DNA-NGS, supplementary RNA-NGS detection can be performed, or simultaneous DNA+RNA dual-dimensional detection can be conducted. This maximizes the discovery of fusion events and improves the clinical benefit rate for patients.
Currently, there are three common combined high-throughput sequencing strategies for DNA/RNA:
01 Sequential Approach:
First perform DNA-NGS on clinical samples. For patients negative for driver gene mutations, use retained samples or re-collect samples for supplementary RNA-NGS detection.
The overall detection cycle is relatively long.
02 Parallel Approach:
Extract DNA and RNA from the same sample, then perform parallel library construction, sequencing, and data analysis for DNA and RNA samples separately (i.e., separate library construction for DNA and RNA followed by individual sequencing and analysis). Library construction for DNA and RNA is completed in independent systems without mutual interference. It improves detection rate and accuracy without affecting the detection cycle.
03 Unified Approach:
Extract DNA and RNA from the same sample, then conduct library construction, sequencing, and data analysis of nucleic acids in the same system and identical operational steps (i.e., combined library construction for DNA+RNA followed by sequencing and analysis).
It requires distinguishing the capture of DNA and cDNA templates to avoid impacts on mutation frequency and copy number variation detection, with limitations on detection regions and the number of genes.
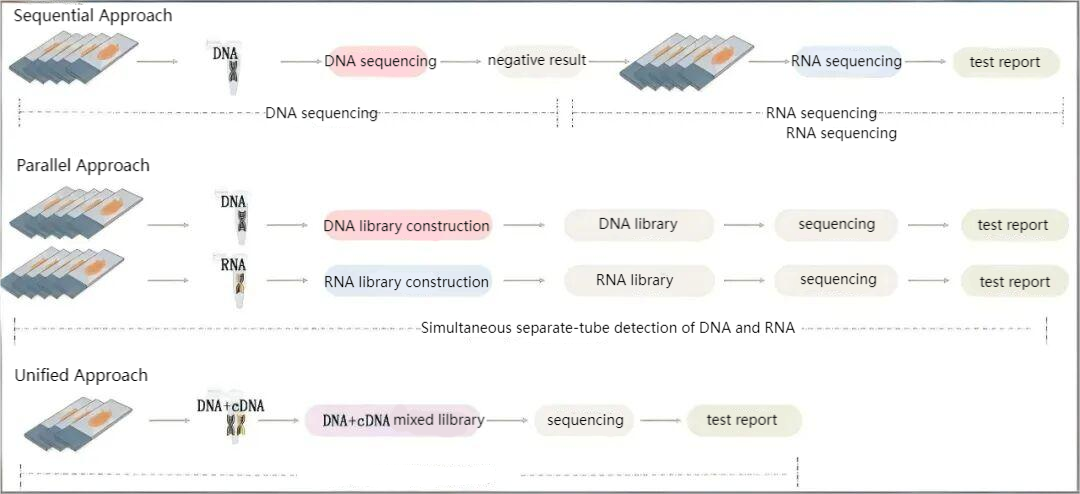
Schematic Diagram of Three Strategy Comparisons for DNA/RNA-NGS Co-Detection
Common Capture Technology Schemes for DNA/RNA High-Throughput Sequencing Detection:
The probe-based method is suitable for sequential/parallel detection schemes. At the DNA level, probes are designed for the CDS regions of detection targets (such as SNVs and InDels) and intronic regions of known fusions, enabling the detection of mutations and variations in known fusion regions. Meanwhile, at the RNA level, probes designed based on transcripts are used for supplementary fusion validation of RNA samples. The detection is performed in separate tubes without mutual interference, and it can be applied for the detection of multiple cancers and pan-cancer heterogeneity.
Although the amplicon-based method can achieve simultaneous DNA/RNA-NGS co-detection by designing DNA-level primers for point mutations/insertions/deletions in exonic and intronic regions respectively, and RNA-level primers for fusion variations in two exons, the detection regions and the number of primers are strictly limited. Additionally, primer performance imposes strict requirements on the quality of DNA and RNA samples extracted from FFPE (formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded) tissues. Therefore, it has high limitations in clinical applications.
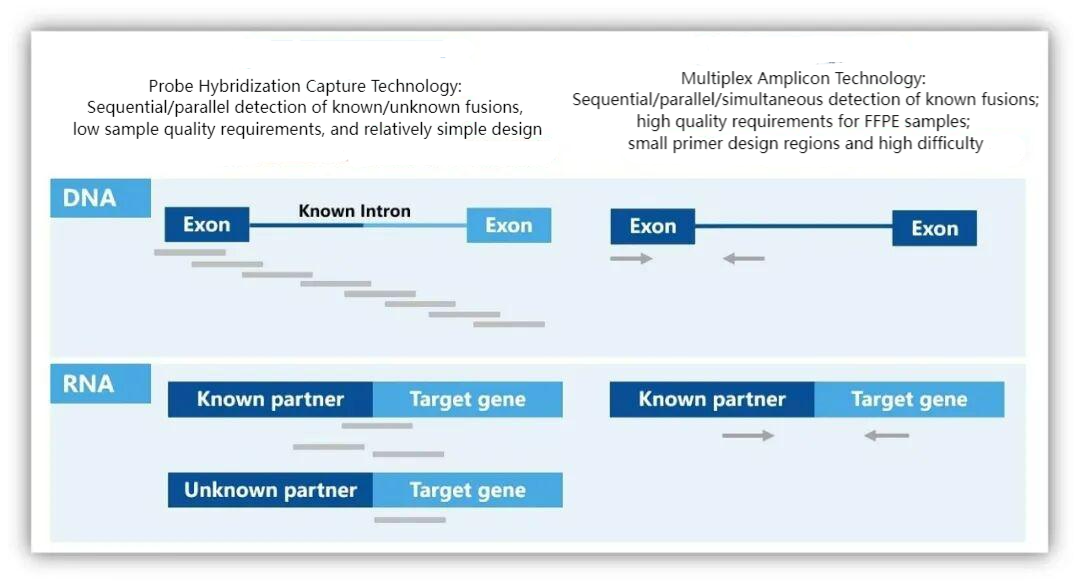
Design Schemes of Different Capture Technologies
With 11 years of accumulation in product development, iGeneTech has gained extensive experience in targeted capture sequencing for DNA-NGS and RNA-NGS. The company has not only realized a full-process reagent solution from sample extraction to library construction and capture but also accumulated differentiated capture schemes for different mutation types in the probe design stage. This ensures stable capture of various complex variations.
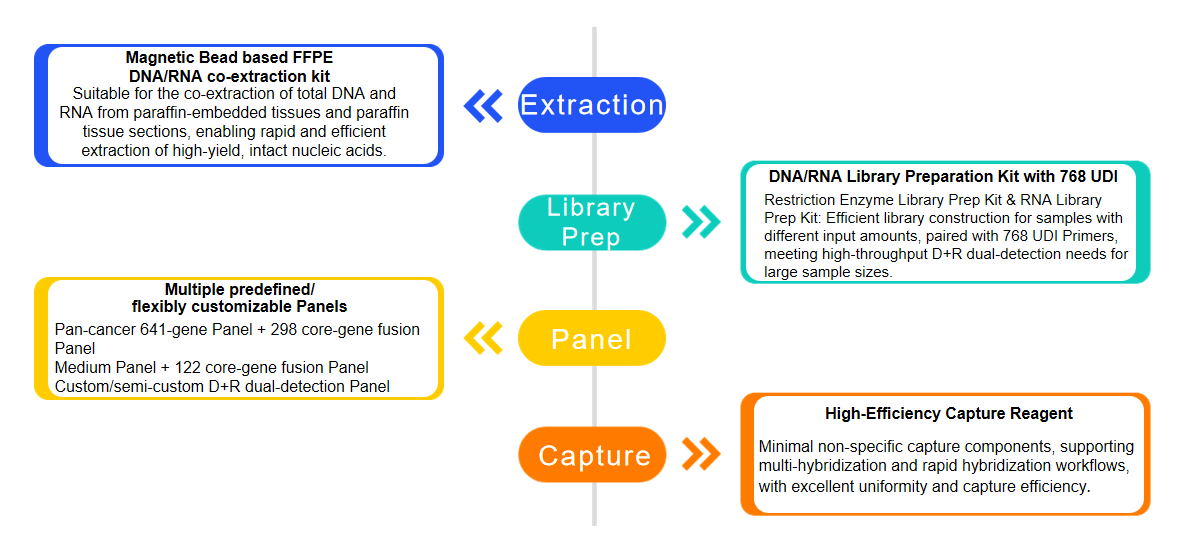
iGeneTech DNA+RNA Dual-Detection Full-Process Reagent Solution
Accurate detection of SNVs, InDels, and known fusions at the DNA level
Table 1: Detection Results of Mutation Sites in gDNA Positive Reference Standards
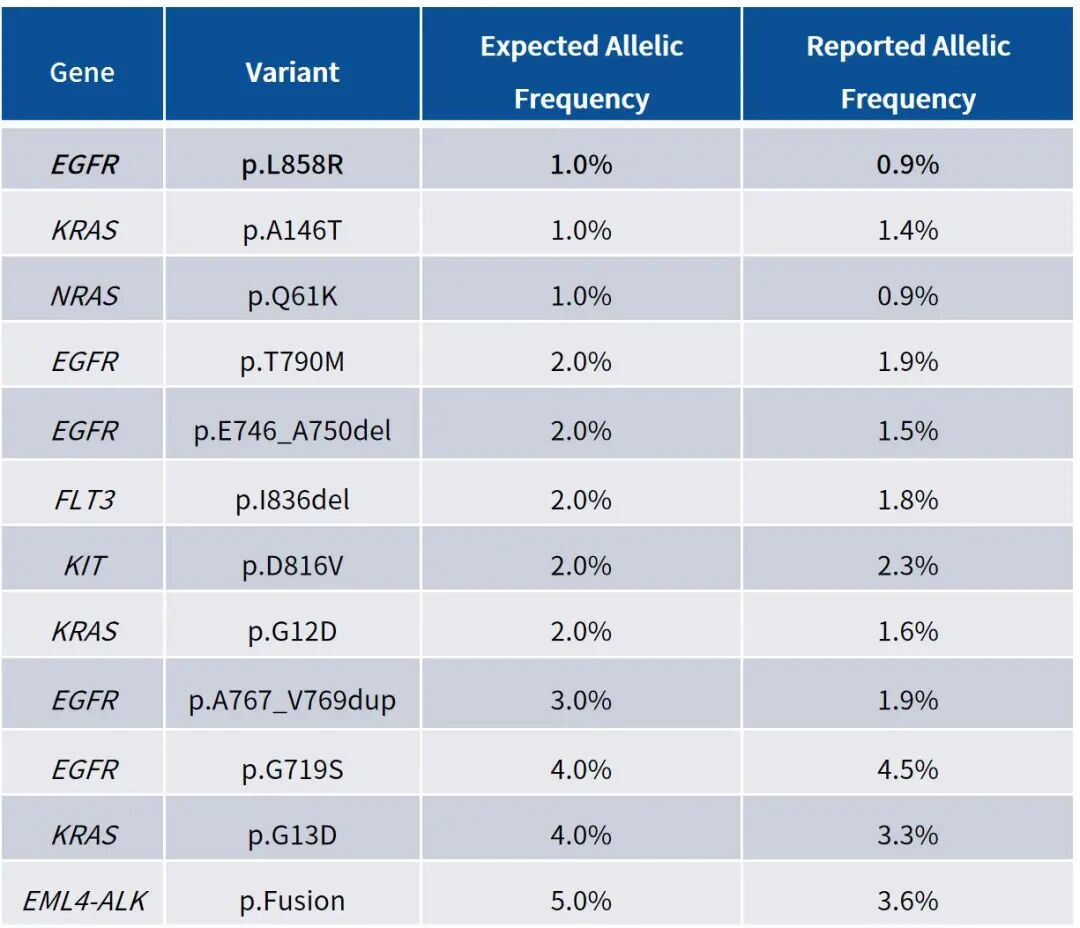
Note: Tests were performed using Shuimu Jiheng gDNA positive reference standards. Library construction was conducted with the Restriction Enzyme V3 Library Prep Kit, followed by capture with the Solid Tumor Mid Panel. Analysis results showed that all positive mutation sites were detected, consistent with expected outcomes.
Accurate detection of fusions at the RNA level
Table 2: Detection Results of RNA Fusion Positive Reference Standards
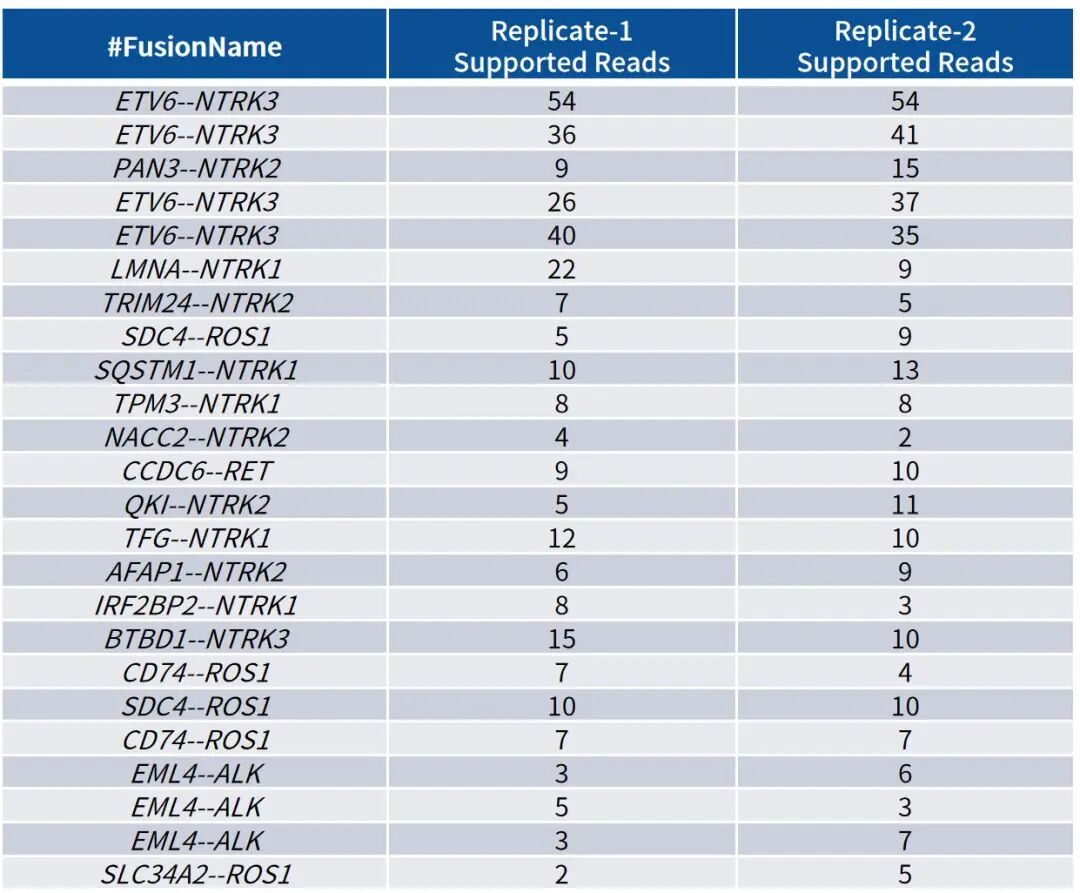
Note: Mixed tests were performed using Shuimu Jiheng RNA fusion reference standards and total RNA from negative samples, with a total input of approximately 100 copies. Library construction was carried out using the RNA Library Prep Kit, followed by capture with the Core Genes Fusion RNA Panel (~4 Gb Raw bases). Fusion analysis was performed with Starfusion. Results showed that all corresponding fusions in the reference standards were successfully detected.
Predefined large and medium pan-cancer DNA+RNA dual-detection Panels: Full-process supporting reagents, ready for use upon order, convenient and flexible.
Customized DNA+RNA dual-detection Panels: Rapid development of high-quality products based on customer-focused genes.
Product Info
Product Name | Speci. | Cat. No. |
Pan-Cancer Panel V2 | 24/96 rxn | PT1011715/PT1011712 |
Solid Tumor Fusion RNA Panel | 24/96 rxn | PH2000475/PH2000472 |
Solid Tumor Mid Panel | 24/96 rxn | PH2002105/PH2002102 |
Core Genes Fusion RNA Panel | 24/96 rxn | PH2000595/PH2000592 |
IGT® Adapter & 10 nt UDI Primer 1-768 (for Illumina, plate) | 768*1 rxn | C11282 |
TargetSeq One® Hyb & Wash Kit v3.0 with Eco Universal Blocking Oligo* | 24/96 rxn | C11614/C11612 |
* Kits compatible with platforms such as Illumina and MGI are available, along with universal reagents for both platforms.

 CN
CN