Plant Whole Exome Sequencing: Focusing on Core Genetic Information and Driving Efficient Scientific Research Output
Why Choose Plant Whole Exome Sequencing?
With the development of genome sequencing technology, researchers can conduct genomic selection research through solutions such as SNP chips, genome resequencing, and whole exome sequencing.
However, in practical applications, SNP chips have limitations: On one hand, their applicability in cross-variety or cross-population studies is narrow, making it difficult to meet the analytical needs of complex populations; On the other hand, their resolution is limited, which prevents fine mapping of smaller genomic regions and thus makes it hard to accurately identify causal variants that regulate target traits [1]. Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) faces challenges of large data volume, high cost, and complex analysis. In contrast, whole exome sequencing achieves accurate sequencing of key coding genes by targeting and enriching the exonic regions of the plant genome. It provides a powerful tool for functional genomics and genetics research, and helps achieve the scientific research goals of "lower cost, higher efficiency, and greater focus on core variants".
Star Product: Custom-Designed, Covering Whole Exome Products for Dozens of Species
Relying on its independently developed TargetSeq® Hybrid Capture Sequencing Technology and IGT® Oligo Pools Synthesis Platform, iGeneTech has launched more than 10 plant whole exome products, including those for wheat, barley, corn, and cotton, with strictly verified performance.
1. Wheat Whole Exome Product
Product Design: Designed based on the IWGSC RefSeq V2.1 reference genome, covering a 132.6 Mb Coding Sequence (CDS) region.
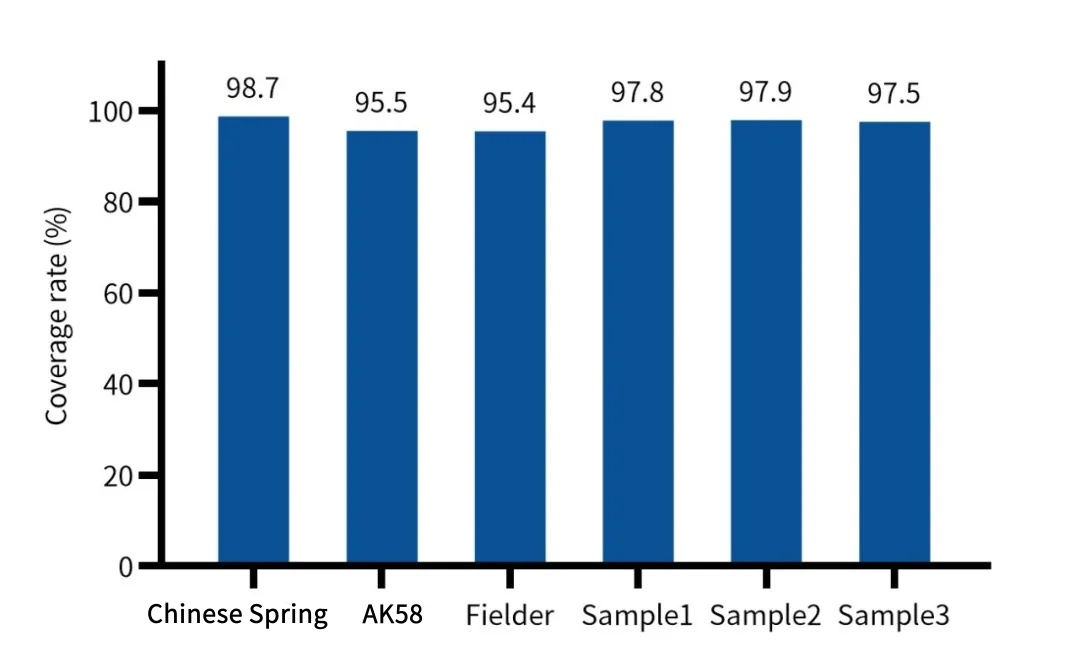
Performance: With a data volume of 7 Gb, an effective depth of over 30× can be achieved; the CDS region coverage rate for different varieties (such as Chinese Spring, Aikang 58) reaches 95.4%-98.7%.
Application Scenarios: Population genetics research, stress-resistant gene screening, variety evolution analysis, etc.
Case Sharing 1. Large-Scale Population Genetics and Evolution Research
By analyzing the genetic variation of natural populations through whole exome sequencing, the origin of species, dispersal routes, and adaptive evolution mechanisms can be revealed.
Researchers performed whole exome sequencing on approximately 500 wheat samples from different geographical regions worldwide. Using genetic variation information at the gene, chromosome, and subgenome levels, they deciphered the possible origin of modern wheat, the impacts of distribution area expansion, and the selected allelic variations since wheat domestication [2]. This study provides new approaches for wheat breeding improvement (published in Nature Genetics).

Case Sharing 2. Mutant Library Construction and Functional Gene Mining
After generating mutant populations using mutagenesis technologies such as EMS (Ethyl Methanesulfonate) and high-energy rays, whole exome sequencing can quickly identify mutation sites and construct a genotype-phenotype association database.
Researchers performed whole exome sequencing on 1,535 tetraploid EMS mutant wheat plants (variety: Kronos) and 1,200 hexaploid EMS mutant wheat plants (variety: Cadenza). They identified over 10 million mutation sites (with an average of 2,705 or 5,351 sites per individual plant), and the mutation frequency was approximately 35-40 SNPs per kilobase (SNP/Kb) [3]. This study provides abundant resources for research on functional genes related to traits such as stress resistance and yield (published in PNAS).

2. Barley Whole Exome Product
Product Design: Designed based on the latest barley reference genome MorexV3, covering a 37.1 Mb Coding Sequence (CDS) region and capable of capturing the CDS regions of over 95% of genes.
Performance: With a data volume of 3 Gb, an effective depth of over 30× can be achieved; the coverage rate and capture efficiency of different varieties all perform excellently.
Application Scenarios: Gene mapping, mutant library construction, adaptive evolution research, etc.
Case Sharing: Fine Gene Mapping
SNP chip capture usually only obtains loci associated with traits, while exome capture can achieve fine mapping and identification of key candidate genes.
In the study on the mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTL) and candidate genes in two-rowed spring barley, to further perform fine mapping of QTL and search for candidate genes, the research team used exome capture sequencing data to increase marker density. Among 31.65% of the QTLs, the markers in the exome region showed stronger association signals than the original 50k SNP chip markers, which made the identification of candidate genes more accurate [4].
3. Maize Whole Exome Product
Product Design
Designed based on the latest maize reference genome B73 V5, it covers a 43.2 Mb CDS (Coding Sequence) region and efficiently captures the CDS regions of over 96% of genes.
Performance
With a data volume of 3 Gb, an effective depth of approximately 30× can be achieved, meeting the requirements for high-precision sequencing.
Application Scenarios
Such as disease-resistant gene cloning, gene function research, analysis of heterosis mechanism, etc.
Case Sharing: Gene Function Research
The plumpness of maize kernels is closely related to yield and quality. Through bulked segregant analysis combined with exome sequencing, the research team identified a C→T mutation in the second exon of the Zm00001d002051 gene (leading to a Ser→Leu substitution at position 282) in the maize dek20 mutant. This study clarified that the Zm00001d002051 gene encodes the rate-limiting enzyme in serine synthesis, revealed the major pathway of serine synthesis in maize, and laid a foundation for subsequent research [5].

"Capture All" Program: Customized Services + Cooperation to Expand Research Boundaries
iGeneTech takes "Capture All" as its philosophy and supports multi-dimensional product cooperation models, including plant whole exomes, custom development of whole exomes + chips, and custom high-throughput chips.
Cooperative Development
It conducts plant exome research in the form of cooperative development. Specific regions (e.g., SNP chip loci) can be added or exome coverage for specific varieties can be enhanced as needed, with shared intellectual property rights.
Diversified Product Line
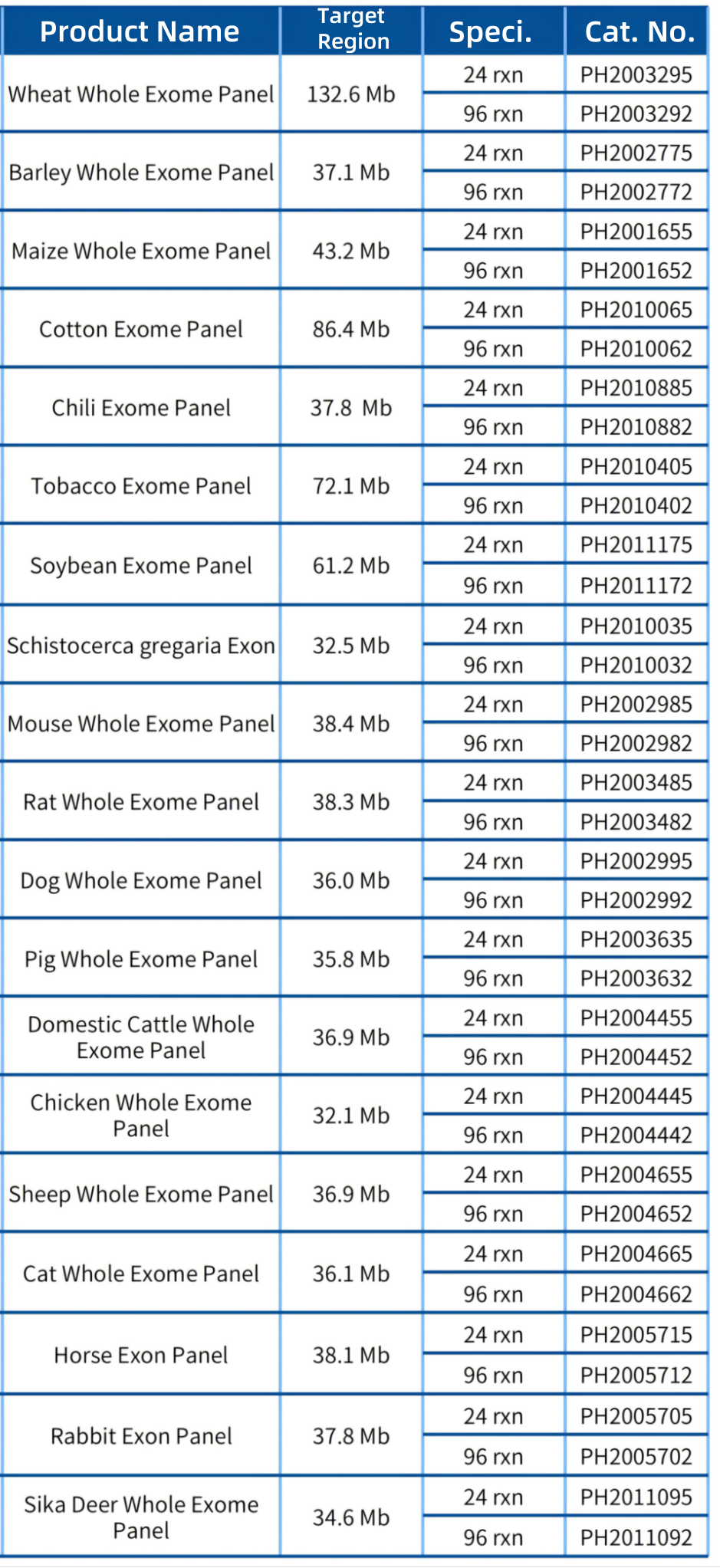
iGeneTech has launched more than 10 whole exome products for animals and plants, including wheat, barley, maize, cotton, pepper, and tobacco (see the table below for the existing product matrix). Cooperation is welcomed for whole exomes of more species.

 CN
CN