What is a Mitochondrial Maternal Haplogroup?
Mitochondrial maternal haplogroup, also known as maternal ancestry, has its core rooted in the unique genetic rules of mtDNA:
Maternal-exclusive inheritance
In most cases, mtDNA is only passed from mothers to all their offspring; fathers' mtDNA does not participate in inheritance, making it equivalent to a "pure maternal genetic clue".
Stable mutation markers
mtDNA has a relatively stable mutation rate during evolution, and these specific mutation loci (such as SNP loci) act like "genetic tags".
Haplogroup = maternal branch
Based on these "tags", scientists group populations sharing a common maternal ancestor into a "mitochondrial haplogroup", with a clear global classification system:
The oldest haplogroup is L0, which originated in Africa and is the "root" of human maternal ancestors.
L1-L6 and other "African lineages" diverged from L0.
After some populations migrated out of Africa, two major lineages (M and N) further differentiated, and then gave rise to common haplogroups such as A, B, C, D, H, and J.
What is Phylotree?
When conducting mitochondrial haplogroup analysis, one cannot bypass the core database—Phylotree (the Phylogenetic Tree of Human Mitochondrial DNA), which serves as the "standard dictionary" for haplogroup classification.
Essence as a "phylogenetic tree"
Phylotree records the differentiation relationships of all discovered global mitochondrial haplogroups in the form of a phylogenetic tree, and marks the characteristic mutation loci corresponding to each haplogroup (e.g., which SNP mutations the H1c haplogroup needs to contain).
Continuously updated "standard"
The latest version is currently 17.2 (some software may still use older versions). Each update incorporates newly discovered haplogroup branches and mutation loci to ensure the accuracy of classification.
Core dependency of software
Nearly all mitochondrial haplogroup analysis software (such as Haplogrep and Haplogrouper evaluated below) needs to call Phylotree data to determine which haplogroup a sample belongs to—the newer the Phylotree version used by the software, the more consistent the analysis results are with the latest scientific research conclusions.
Practical Evaluation of 4 Software Tools
We used the iGeneTech Human Mitochondrial Genome Full-Length Capture Kit to perform mutation analysis on 2800M positive samples and 1 test sample. We selected 4 mainstream mitochondrial haplogroup analysis software tools and provide a one-stop comparison from input format, operation mode, core features to practical test results:
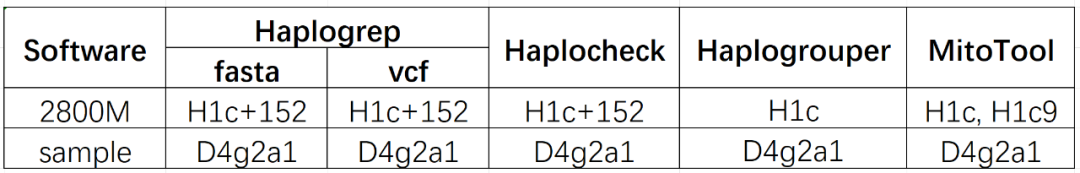
Table: Comparison of Mitochondrial Haplogroup Analysis Results of 4 Software Tools
01 Haplogrep
Core Advantages
Flexible Input
Supports two commonly used formats (VCF (compressed/uncompressed) and FASTA), meeting the needs of different data sources.
Dual Operation Modes
Web Version: No installation required; accessible directly via browser (official website: https://haplogrep.i-med.ac.at/). It features a user-friendly interface that can be easily operated by users without bioinformatics background, and also supports batch upload of multiple samples.
Local Version: Runs on Linux command line, suitable for batch processing of large volumes of data.
Detailed Results
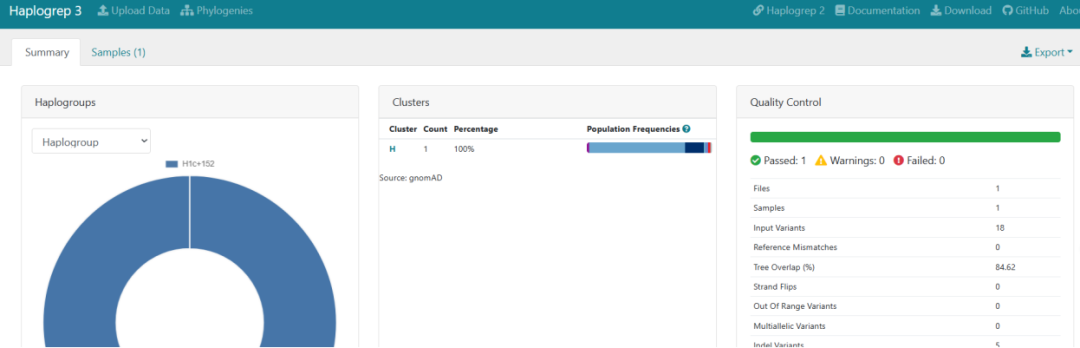
It not only provides haplogroup classification (e.g., H1c+152) but also includes mutation locus annotation, population frequency (linked to the gnomAD database), and quality control information (e.g., coverage, mutation matching rate).
Running Command:
Bash
haplogrep classify --in sample.vcf.gz --format vcf --out haplogrep-vcf.txt
haplogrep classify --in sample.consensus.fa --format fasta –out haplogrep-fa.txt
Web Version Result Display
Top2: Haplocheck
Core Advantages
Flexible Input
Supports two commonly used formats (VCF (compressed/uncompressed) and FASTA), meeting the needs of different data sources.
Operation Method
Runs via Linux command line.
Unique Function
In addition to haplogroup classification, the results can generate an HTML interactive report. The phylogenetic tree can be directly viewed in a browser, which intuitively displays the branch position of the sample's haplogroup.
Running Command:
Bash
haplocheck --raw –out haplocheck.out.xls sample.raw.vcf.gz
Report Result Display

Top3: Haplogrouper
Core Advantages
Input Format
Only supports VCF format.
Operation Method
Runs on Linux command line (based on Python, requires dependency installation).
Unique Features
It can not only analyze mitochondrial maternal haplogroups but also support Y-chromosomal paternal haplogroup analysis. The software comes with the built-in Phylotree17 database (invoked via -l and -t parameters), eliminating the need for additional downloads.
Running Command (Bash)
Bash
python haploGrouper.py -v sample.vcf.gz -t data/chrMT_phylotree17_tree.txt -l data/chrMT_phylotree17_loci.txt -f NC_012920.fa -o sample.haplogroup.txt -x sample.allscore.txt
Tips: If the VCF file is a merged file containing multiple samples, you can create a list of sample names and specify it with the -i parameter.
Top4: MitoTool
Core Advantages
Input Format
Supports FASTA format.
Operation Method
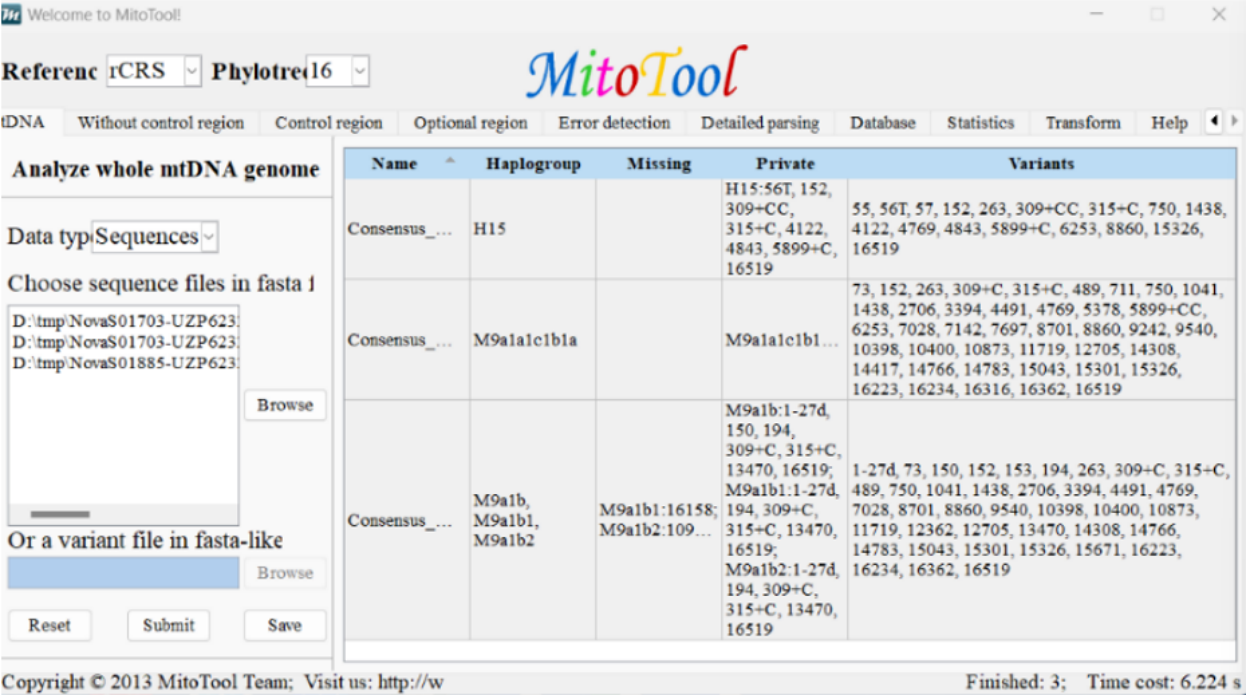
Available for download and installation on Windows/Mac, featuring a fully visualized interface. Analysis can be initiated by uploading a FASTA file and clicking "Submit".
Simple Operation.
The results will list information such as haplogroups and missing loci.
Minor Disadvantages
The dependent Phylotree database is version 16 (relatively outdated), which may fail to identify newly discovered haplogroup branches.
It does not support VCF format, resulting in data format limitations.
Software Interface Schematic Diagram
Introduction to Related Products
iGeneTech has developed two sets of mitochondrial capture protocols based on hybridization capture sequencing technology and multiplex amplicon sequencing technology, which can fully capture the 16,569 bp full-length human mitochondrial genome, providing customers with a highly efficient and high-quality comprehensive solution for the full-length human mitochondrial genome.
iGeneTech’s comprehensive solution for the full-length human mitochondrial genome has distinct advantages:
Complete Capture of Mitochondrial Genes
iGeneTech Human Mitochondrial Genome Full-Length Capture Kit achieves 100% coverage of the entire mitochondrial genome.
Excellent Capture Performance
Superior data output, high capture efficiency, and outstanding uniformity.
Flexible Capture Protocols
Hybridization capture sequencing protocol and multiplex amplicon sequencing protocol.

 CN
CN





