Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) is the optimal curative option for approximately 50% of adult patients with acute leukemia, as well as those with intermediate/high-risk disease or drug-resistant/relapsed conditions. Globally, around 90,000 patients undergo this treatment annually, with 75% used for leukemia and 94% involving ALL, AML, and MDS [1,2,3].
However, transplantation poses multiple challenges: Relapse is the primary cause of treatment failure—about 40% of AML patients relapse post-transplantation, with a 2-year survival rate of less than 20% after relapse. Complications such as conditioning toxicity, infections, and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) also threaten patients’ treatment efficacy and long-term survival [4,5,6].
In clinical practice, chimerism status assessment is crucial: Mixed myeloid chimerism in malignant diseases is a key risk signal requiring further investigation. For patients with hemoglobinopathies, regular monitoring of whole-blood and lineage-specific chimerism is necessary at specific post-transplant time points and during immunosuppressive therapy to guide immunosuppressant management [7].
Therefore, precise and sensitive chimerism detection technology serves as the core support for evaluating transplantation outcomes, early warning of relapse risks, and guiding clinical decision-making.
Core Process of allo-HSCT
Pre-transplant Preparation
Clarify disease type/stage, evaluate heart, liver and kidney functions, and confirm transplantation indications
Donor Screening & Matching
Priority is given to related donors; if unavailable, unrelated donors are sourced from bone marrow banks. Core HLA testing is performed to ensure matching degree
Conditioning
High-dose chemotherapy/radiochemotherapy combination to eliminate malignant/abnormal hematopoietic cells, suppress autoimmunity, and pave the way for stem cell implantation
Stem Cell Collection & Infusion
Collect bone marrow/peripheral blood/umbilical cord blood stem cells from donors, process them, and infuse intravenously into the patient
Post-transplant Recovery & Monitoring
Monitor vital signs + hematopoietic function; prevent and treat complications (conditioning toxicity, infection, GVHD); use chimerism testing to evaluate implantation efficacy and relapse risk
Long-term Follow-up
Long-term monitoring of hematopoietic/immune functions and disease status; adjust treatment plans to ensure long-term survival
Clinical Application Value of Chimerism Detection
01 Implantation Efficacy Assessment
As a core indicator for determining stem cell implantation, it clarifies whether complete chimerism is achieved after transplantation, or whether mixed chimerism, chimerism rate decline and other conditions exist by detecting the proportion of donor/recipient cells. It timely alerts the risk of transplant rejection and serves as a key basis for judging the success of transplantation.
02 Relapse Risk Early Warning
Dynamically monitor changes in the chimerism rate—an abnormal increase in the proportion of recipient-derived cells is an important signal of early disease relapse. It can prompt risks before patients develop clinical symptoms, gain time for early intervention therapy (such as donor lymphocyte infusion), and reduce the relapse rate.
03 Guidance for Clinical Treatment Decision-Making
Based on the chimerism status results, it guides the dose adjustment of immunosuppressants, the selection of drug withdrawal time, or the decision on whether to initiate regimens such as second transplantation and targeted therapy, helping to achieve individualized and precise treatment.
04 Correlation Assessment of Complications and Immune Reconstitution
It assists in judging the progress of immune reconstitution, and can indirectly reflect the occurrence risk of complications such as graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), providing a reference for the prevention and management of complications and improving the overall treatment safety.
Technical Solution Comparison
Current mainstream chimerism detection technologies each have their own characteristics. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology based on single nucleotide variants (SNV) and insertions/deletions (InDels) has gradually become the clinical preferred solution by virtue of its advantages such as high sensitivity and high resolution. The comparison of core parameters of each technology is as follows:
Technology | Marker | Sensitivity | Advantages | Disadvantages |
STR-PCR | Short Tandem Repeat (STR) | 1%-5% | Gold standard; quantitative analysis of multiple cell lineages; relatively low cost | Time-consuming; requires high-purity DNA |
Real-time Quantitative PCR (qPCR) | Single Nucleotide Variant (SNV), Insertion/Deletion (InDel) | 0.1% | High sensitivity; real-time monitoring and quantification | Technically complex; insufficient standardization |
Digital PCR (dPCR) | SNV, Insertion/Deletion (InDel) | 0.01%-0.1% | High sensitivity, low DNA requirement; supports multiplex detection and lineage-specific analysis | High cost; requires pre-selection of variants |
Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) | Sex Chromosomes | ≤5% | Suitable for sex-mismatched transplantation; intuitively displays cell origin | Limited to sex-mismatched transplantation cases |
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) | SNV, Insertion/Deletion (InDel) | 0.01%-1% | High resolution; simultaneous detection of multiple markers; dynamic monitoring of minimal residual disease (MRD) | Relatively complex data analysis |
Product Introduction
Based on years of mature genome-wide probe selection experience and real-world data accumulation, iGeneTech has launched an SNP-based NGS chimerism detection solution. With the product features of high sensitivity, high stability, and high flexibility, it provides a higher-quality detection option for clinical applications.
01 Selected Markers · 500 High-Quality SNPs
Even distribution and stable performance.The solution selects 500 core detection markers (supports flexible customization / semi-customization). Marker selection criteria:
· High minor allele frequency (MAF):Ensures broad population applicability, with 0.45 ≤ AF (eas) ≤ 0.55.
· Uniform chromosomal distribution:Markers are evenly distributed across all autosomes to avoid detection blind spots.
· Stable capture performance:Normalized capture depth ≥ 1.04, standard deviation (std) ≤ 0.2, guaranteeing reliable detection results
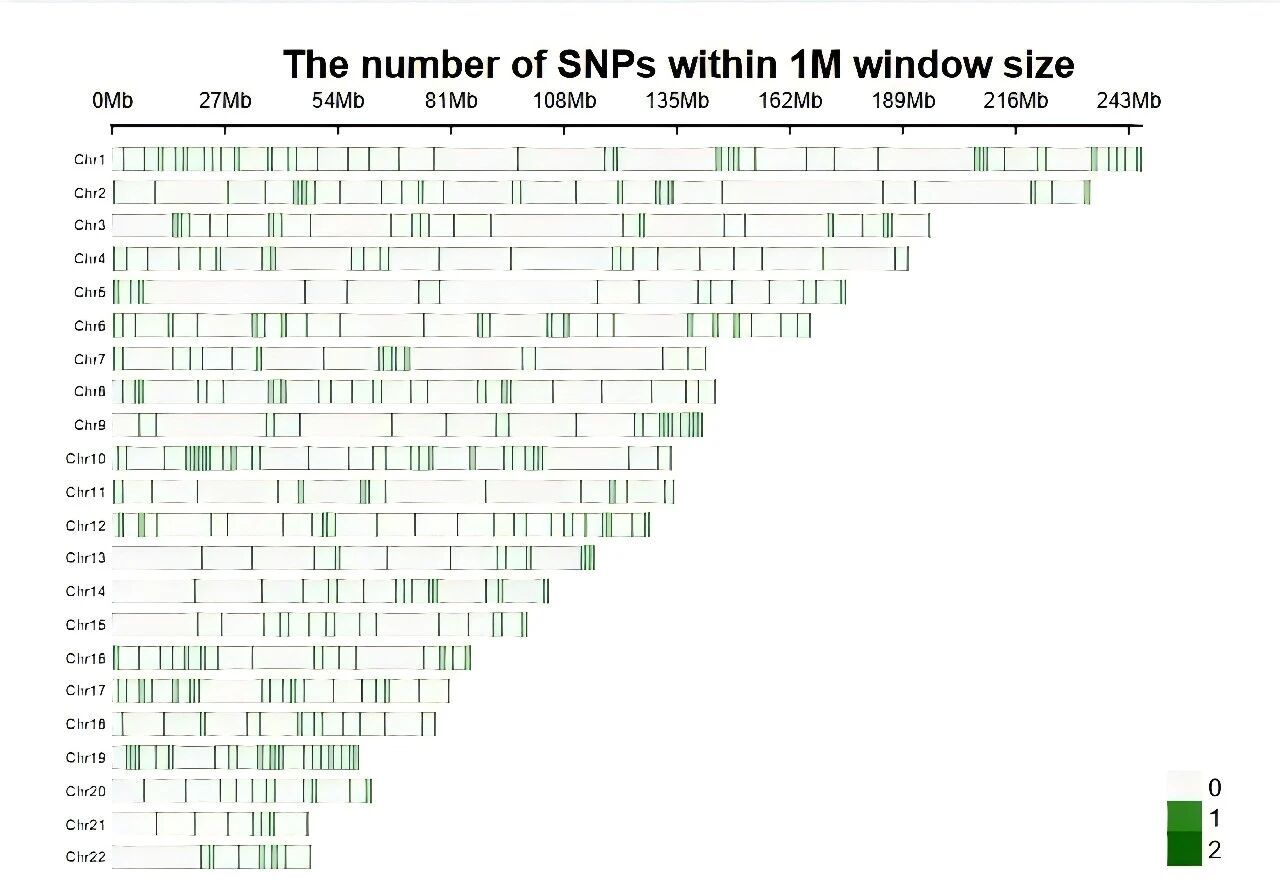

Figure 1. Chromosomal distribution of 500 markers
02 Excellent Capture Performance · High On‑Target Rate + High Uniformity
The solution supports multiple library prep strategies and UMI (Unique Molecular Identifier) technology to meet detection requirements for various sample types.
Meanwhile, high-quality, high-density DNA probes and high-efficiency capture reagents are applied to significantly improve detection performance.
According to real-world test data, key indicators including effective read on‑target rate and coverage show excellent performance, laying a solid foundation for accurate detection.
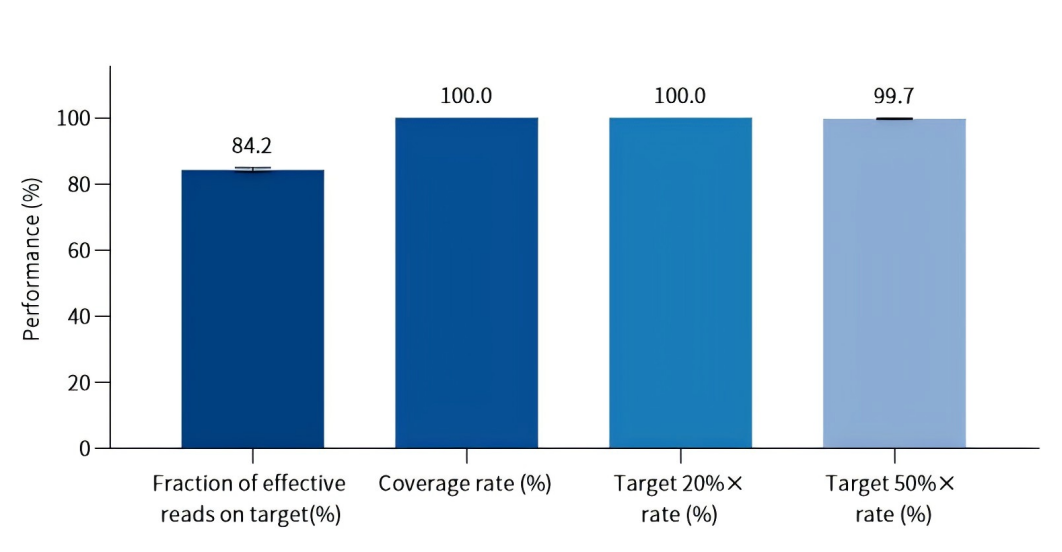
Figure 2. Capture performance evaluation. gDNA samples were fragmented and used for library construction with 50 ng input. Capture was performed using the Chimerism SNP Panel with TargetSeq One® Hyb & Wash Kit v3.0.
03 Ultra-High Sensitivity · Accurate detection of 0.01% chimerism for early risk warning
Based on the UMI analysis workflow, the solution enables sensitive detection of chimerism as low as 0.01% in mixed samples.
Gradient mixing tests using two healthy donor samples to simulate chimeric states (shown in the table below) demonstrate that the detection results are highly consistent with the theoretical mixing ratios. This fully validates its accuracy in detecting trace chimeric cells and supports earlier identification of relapse risk in clinical practice.
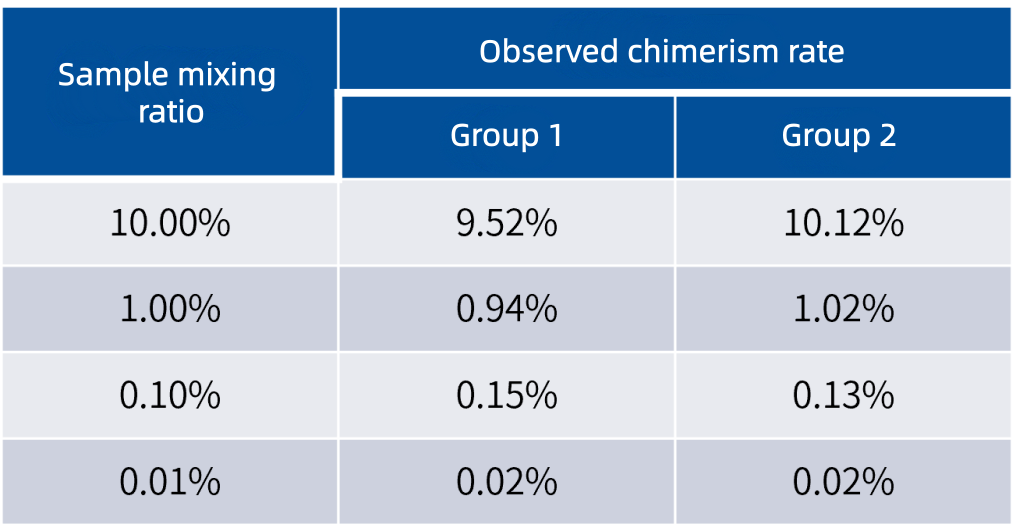
Note: Two sets of normal human samples were used for gradient mixing tests to simulate chimerism. Mutation analysis was performed on donor, recipient, and mixed samples respectively to comprehensively evaluate the chimerism rate.
04 Wide Application · Supports flexible / semi-customization to cover diverse scenarios
Post-organ transplantation monitoring: Detection based on circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) samples reduces the frequency of post-transplant biopsies and minimizes trauma to patients.
Sample quality control: Used to identify sample contamination and mix-up issues, ensuring the accuracy of experimental data.
Product Info
Product Name | Speci. | Cat.No |
Chimerism SNP Panel | 24/96 rxn | PH2012675/ PH2012672 |
IGT® Enzyme Plus Library Prep Kit V3 | 16/96 rxn | C11111/C11112 |
IGT® UMI Adapter & UDI Primer 1-96 * | 96*1 rxn | C10092 |
TargetSeq One® Hyb & Wash Kit v3.0 with Eco Universal Blocking Oligo* | 4/96 rxn | C11614/C11612 |
TargetSeq® Cap Beads & Nuclease-Free Water | 5 mL each | C10422 |

 CN
CN



